
Virtualization is a fundamental technology that has transformed how computer resources are managed and deployed in cloud computing environments. Virtualization increases flexibility, scalability, and efficiency in the deployment and management of IT infrastructure by abstracting actual hardware and generating virtual versions of servers, storage, and networks. In this essay, we will look at the notion of virtualization and its different levels within cloud computing, throwing light on its significance and ramifications for organizations in today’s digital age.
Understanding Virtualization
Definition of Virtualization
Virtualization is fundamentally about creating virtual replicas of actual hardware components like servers, storage devices, and networks. These virtual instances, also known as virtual machines (VMs) or virtualized resources, operate independently of the underlying physical infrastructure and can execute different operating systems and applications at the same time.
Read More: 4 Best tools to learn DevOps – How to start DevOps?
How Does Virtualization Work?
Virtualization is based on hypervisor software, which abstract physical hardware resources and allocate them to virtual computers. Hypervisors allow virtualized resources to be isolated and managed independently on the same physical hardware.
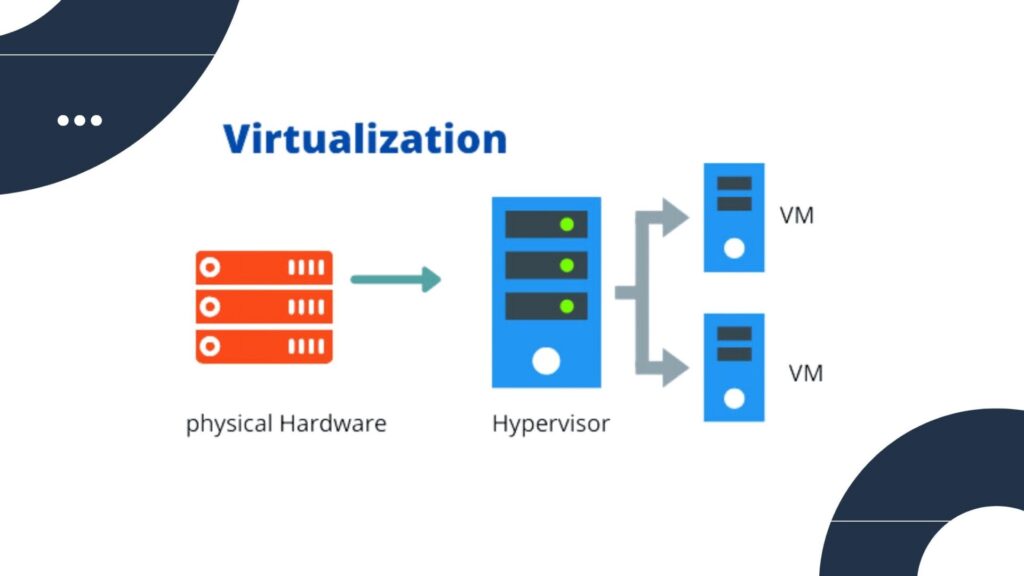
Benefits of Virtualization
The implementation of virtualisation offers many important benefits to organizations
- Resource Consolidation: Virtualization allows several physical servers to be consolidated onto a single hardware platform, saving space and electricity.
- Improved Flexibility: Virtualized environments can readily scaled up or down to meet changing workloads and resource needs, resulting in increased agility and responsiveness.
- Enhanced Disaster Recovery: Virtualization makes it easier to create virtual backups and snapshots, which allows for speedier recovery times and reduces downtime in the case of hardware failures or disasters.
Levels of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
There are many layers of virtualization in cloud computing, each with its own set of capabilities and features. Let’s look at these stages in greater detail:
Read More: DevOps engineer vs Cloud Engineer: which is better?
Hardware Virtualization
Hardware virtualization is the abstraction of physical hardware resources such as servers, storage, and networking components into virtualized instances known as virtual machines (VMs). Each VM is an autonomous entity with its own operating system and programs, allowing numerous VMs to run on the same physical server.
Operating System Virtualization
Operating system (OS) virtualization, commonly referred to as containerization, is a lightweight alternative to traditional hardware virtualization. Instead of building separate virtual machines, containerization allows you to create isolated user-space instances, or containers, on a single host operating system. Containers share the host OS kernel, resulting in lower overhead and faster deployment times than standard VMs.
Application Virtualization
Application virtualization entails separating individual apps and their dependencies into self-contained pieces known as virtualized application packages. These packages, often known as “virtualized apps” or “app containers,” may be distributed and performed on any suitable machine, eliminating the need for traditional installation procedures. Application virtualization streamlines software deployment, lowers compatibility difficulties, and improves security by separating programs from the underlying operating system.
Advantages of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization is crucial in allowing the delivery of cloud services and resources, delivering various benefits for businesses
- Scalability: Virtualized environments may be dynamically scaled to handle changing workloads and demand surges, assuring peak performance and resource utilization.
- Resource Efficiency: Virtualization allows enterprises to make the most use of their hardware resources by combining several virtual instances on a single physical server, lowering costs and decreasing waste.
- Agility and Flexibility: Virtualization enables organizations to quickly provision, deploy, and transfer computer resources, resulting in a quicker time-to-market and higher response to changing business demands.
Read More: 9 reasons why you need cloud computing for small business
Challenges and Considerations
While virtualization provides various benefits, it also poses some obstacles and issues that enterprises must address
- Security Concerns: Virtualized systems provide new security threats, such as hypervisor vulnerabilities and VM escape attacks. To reduce these threats, it is critical to implement strong security mechanisms such as network segmentation, encryption, and access control.
- Performance Overheads: The abstraction layer that separates virtual instances from actual hardware might create performance overheads. Resource allocation optimization, hypervisor tuning, and the use of hardware-assisted virtualization technologies can all help to reduce these overheads.
- Complexity and Management Overhead: Managing virtualized environments may be challenging, especially at scale. Organizations must invest in effective management tools and procedures to improve administration, monitoring, and maintenance.
To summarize, virtualization is a basic technology that supports cloud computing, allowing enterprises to maximize resource efficiency, increase flexibility, and drive innovation. Understanding the various degrees of virtualization and its consequences for cloud settings allows organizations to use virtualization to achieve strategic goals and acquire a competitive advantage in today’s digital economy.
